Dim workbook As New Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Workbook()
Dim worksheet As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Worksheet = _
workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
A common task in a Microsoft® Excel® workbook is to store a column or row of numerical data and have a cell containing the total of these numbers. The nice thing about this total is it can automatically update when one of the numbers changes. You can create a total cell in a worksheet by applying a formula as the cell’s value.
Using this topic, you will learn how to create cells contains totals of data in the worksheet.
Create a workbook with a worksheet.
Create a new website .
Add a Button to the form.
Double-click the Button to open the code-behind for its Click event.
Create a Workbook with one Worksheet:
In Visual Basic:
Dim workbook As New Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Workbook()
Dim worksheet As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Worksheet = _
workbook.Worksheets.Add("Sheet1")
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Workbook workbook = new Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Workbook(); Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Worksheet worksheet = workbook.Worksheets.Add( "Sheet1" );
Define the columns for the worksheet data.
Make column headers so the data is easily identified:
In Visual Basic:
Dim headersRow As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRow = worksheet.Rows.Item(0) headersRow.Cells.Item(0).Value = "Order ID" headersRow.Cells.Item(1).Value = "Product" headersRow.Cells.Item(2).Value = "Unit Price" headersRow.Cells.Item(3).Value = "Quantity" headersRow.Cells.Item(4).Value = "Discount" headersRow.Cells.Item(5).Value = "Order Total"
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRow headersRow = worksheet.Rows[ 0 ]; headersRow.Cells[0].Value = "Order ID"; headersRow.Cells[1].Value = "Product"; headersRow.Cells[2].Value = "Unit Price"; headersRow.Cells[3].Value = "Quantity"; headersRow.Cells[4].Value = "Discount"; headersRow.Cells[5].Value = "Order Total";
Set special formatting for any columns which require it:
In Visual Basic:
' The "Unit Price" column should display its values as dollars
worksheet.Columns.Item(2).CellFormat.FormatString = _
"""$""#,##0.00_);(""$""#,##0.00)"
' The "Discount" column should display its values as percentages
worksheet.Columns.Item(4).CellFormat.FormatString = "0.00%"
' The "Order Total" column should display its values as dollars
worksheet.Columns.Item(5).CellFormat.FormatString = _
"""$""#,##0.00_);(""$""#,##0.00)"
' Allow enough room to display the totals
worksheet.Columns.Item(5).Width = 3000
In C#:
// The "Unit Price" column should display its values as dollars worksheet.Columns[2].CellFormat.FormatString = "\"$\"#,##0.00_);(\"$\"#,##0.00)"; // The "Discount" column should display its values as percentages worksheet.Columns[4].CellFormat.FormatString = "0.00%"; // The "Order Total" column should display its values as dollars worksheet.Columns[5 ].CellFormat.FormatString = "\"$\"#,##0.00_);(\"$\"#,##0;00)"; // Allow enough room to display the totals worksheet.Columns[5].Width = 3000;
Populate the cells with data.
Populate the cells with data (not the cells that will contain totals; those will be calculated by formulas later):
In Visual Basic:
Dim currentRow As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRow currentRow = worksheet.Rows.Item(1) currentRow.Cells.Item(0).Value = 10248 currentRow.Cells.Item(1).Value = 42 currentRow.Cells.Item(2).Value = 9.8 currentRow.Cells.Item(3).Value = 10 currentRow.Cells.Item(4).Value = 0.075 currentRow = worksheet.Rows.Item(2) currentRow.Cells.Item(0).Value = 10248 currentRow.Cells.Item(1).Value = 72 currentRow.Cells.Item(2).Value = 34.8 currentRow.Cells.Item(3).Value = 5 currentRow.Cells.Item(4).Value = 0.075 currentRow = worksheet.Rows.Item(3) currentRow.Cells.Item(0).Value = 10249 currentRow.Cells.Item(1).Value = 14 currentRow.Cells.Item(2).Value = 18.6 currentRow.Cells.Item(3).Value = 9 currentRow.Cells.Item(4).Value = 0.1 currentRow = worksheet.Rows.Item(4) currentRow.Cells.Item(0).Value = 10249 currentRow.Cells.Item(1).Value = 51 currentRow.Cells.Item(2).Value = 42.4 currentRow.Cells.Item(3).Value = 40 currentRow.Cells.Item(4).Value = 0.1
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRow currentRow; currentRow = worksheet.Rows[1]; currentRow.Cells[0].Value = 10248; currentRow.Cells[1].Value = 42; currentRow.Cells[2].Value = 9.80; currentRow.Cells[3].Value = 10; currentRow.Cells[4].Value = 0.075; currentRow = worksheet.Rows[2]; currentRow.Cells[0].Value = 10248; currentRow.Cells[1].Value = 72; currentRow.Cells[2].Value = 34.80; currentRow.Cells[3].Value = 5; currentRow.Cells[4].Value = 0.075; currentRow = worksheet.Rows[3]; currentRow.Cells[0].Value = 10249; currentRow.Cells[1].Value = 14; currentRow.Cells[2].Value = 18.60; currentRow.Cells[3].Value = 9; currentRow.Cells[4].Value = 0.1; currentRow = worksheet.Rows[4]; currentRow.Cells[0].Value = 10249; currentRow.Cells[1].Value = 51; currentRow.Cells[2].Value = 42.40; currentRow.Cells[3].Value = 40; currentRow.Cells[4].Value = 0.1;
Create a Grand Total label under the data.
Create a merged cell, update the data, and apply a label:
In Visual Basic:
Dim mergedCell As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetMergedCellsRegion = _ worksheet.MergedCellsRegions.Add(5, 0, 5, 4) mergedCell.Value = "Grand Total"
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetMergedCellsRegion mergedCell = worksheet.MergedCellsRegions.Add( 5, 0, 5, 4 ); mergedCell.Value = "Grand Total";
Adjust the text alignment so the label appears closer to where the Grand Total cell will be:
In Visual Basic:
mergedCell.CellFormat.Alignment = _ Infragistics.Documents.Excel.HorizontalCellAlignment.Right
In C#:
mergedCell.CellFormat.Alignment = Infragistics.Documents.Excel.HorizontalCellAlignment.Right;
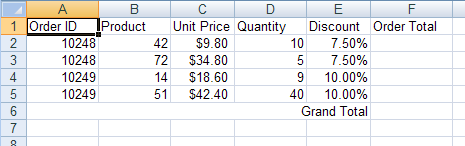
Apply a formula to calculate the sub total of each order record.
Create a formula that calculates the order total. The formula will multiply the unit price by the quantity, and remove the discount from the total: =** (1-[Discount]). The formula will be created as if it were calculating the order total for the first order (the total in cell F2). However, the formula will be created using relative cell references, so when it is applied to the other order total cells, the cell references will be correctly shifted downwards:
In Visual Basic:
Dim orderTotalFormula As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula = _
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula.Parse("=C2$$*$$D2$$* $$(1-E2)", _
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.CellReferenceMode.A1)
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula orderTotalFormula = Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula.Parse( "=C2*D2* (1-E2)", Infragistics.Documents.Excel.CellReferenceMode.A1 );
Create a cell region that defines the cells to which the formula will be applied:
In Visual Basic:
Dim region As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRegion = _ New Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRegion(worksheet, 1, 5, 4, 5)
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRegion region = new Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetRegion( worksheet, 1, 5, 4, 5 );
Apply the formula to the region of order total cells:
In Visual Basic:
orderTotalFormula.ApplyTo(region)
In C#:
orderTotalFormula.ApplyTo( region );
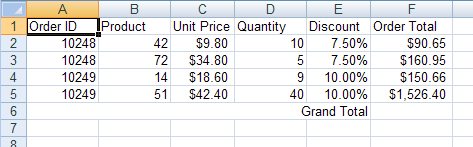
Apply a formula to determine the grand total.
Create a formula to total all "Order Total" cells for a grand total. This formula will use absolute references by prefacing row and column identifiers with a dollar sign ($), but relative references can be used as well:
In Visual Basic:
Dim grandTotalFormula As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula = _
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula.Parse("=SUM($F$2:$F$5)", _
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.CellReferenceMode.A1)
In C#:
Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula grandTotalFormula = Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Formula.Parse( "=SUM($F$2:$F$5)", Infragistics.Documents.Excel.CellReferenceMode.A1 );
Apply the formula to the grand total cell:
In Visual Basic:
grandTotalFormula.ApplyTo(worksheet.Rows.Item(5).Cells.Item(5))
In C#:
grandTotalFormula.ApplyTo( worksheet.Rows[5].Cells[5] );

Save the workbook
Write the workbook to a file:
In Visual Basic:
workbook.Serialize("C:\Orders.xls")
In C#:
workbook.Serialize( "C:\\Orders.xls" );