Dim workbook As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Workbook = ExcelExampleTable.CreateExampleWorkbook()
' Get a table. Table is created in separate code snippet.
Dim table As Infragistics.Documents.Excel.WorksheetTable = workbook.GetTable("Patients")
' Apply Date Period Filter
' If you choose DatePeriodFilterType.Month, second argument represents months from January, 1, to December, 12
' and can take values 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
' If you choose DatePeriodFilterType.Quarter, second argument represents the four quaters of the year - Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4,
' and can take values 1, 2, 3 and 4.
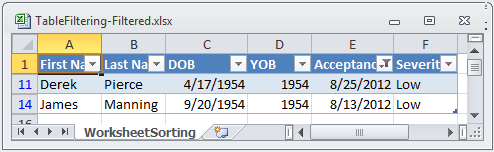
' Code below accepts all dates in August.
table.Columns("Acceptance Date").ApplyDatePeriodFilter(Infragistics.Documents.Excel.Filtering.DatePeriodFilterType.Month, 8)
workbook.Save("C:\TableFiltering-Filtered.xlsx")