Dim northWindDbConnection As New System.Data.SqlClient.SqlConnection( _
"Data Source=.\SQLEXPRESS;AttachDbFilename=""C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL.1\MSSQL\Data\Northwind.mdf"";Integrated Security=True;Connect Timeout=30;User Instance=True")
Dim dataSet As New DataSet()
northWindDbConnection.Open()
Try
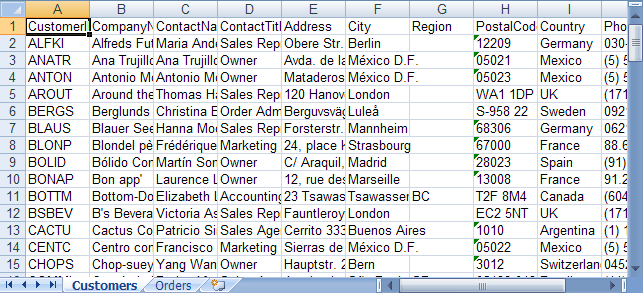
Dim customersSelectCommand As New System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand("SELECT $$*$$ FROM Customers", northWindDbConnection)
Dim customersReader As System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataReader = customersSelectCommand.ExecuteReader()
' Load all data from the customers table in the database
Dim customersTable As New DataTable("Customers")
customersTable.Load(customersReader)
' Add the customers data table to the data set
dataSet.Tables.Add(customersTable)
Dim ordersSelectCommand As New System.Data.SqlClient.SqlCommand("SELECT $$*$$ FROM Orders", northWindDbConnection)
Dim ordersReader As System.Data.SqlClient.SqlDataReader = ordersSelectCommand.ExecuteReader()
' Load all data from the customers orders in the database
Dim ordersTable As New DataTable("Orders")
ordersTable.Load(ordersReader)
' Add the orders data table to the data set
dataSet.Tables.Add(ordersTable)
Finally
northWindDbConnection.Close()
End Try